OpenFMB
Message Bus is a critical middleware component in the distributed systems architecture on various systems and environments. Open Field Message Bus (open FMB) is an extensive framework for robust communication between the microgrid controller and assets on the communication layer. OpenFMB was developed to reduce the complexities of microgrid communication, such as low standards with the data structure combined with the communication protocols towards the grid utilities. For instance, open FMB can be used to translate traditional protocols, including Modbus and DNP3 and NATS.
To facilitate integration of OpenFMB systems with the agents of this interoperability framework, capabilities are currently being added to VOLTTRON to facilitate interaction with OpenFMB aware devices. These capabilities will include message bus adapters to enable communication with common OpenFMB message buses, such as MQTT, and facilities for passing and interacting with data objects encoded using protocol buffers from within VOLTTRON agents.
Architecture
Message buses provide asynchronous communication that performs message transfer between the senders and receivers without a need for immediate response from the receivers as soon the sender sends the message. The components in the message bus are independent which supports scalability and system resilience. Generally, message bus works based on the publisher and subscriber. Open FMB is designed for three different layers, application, adapter and interface layers. The architechture is shown in Figure 1.
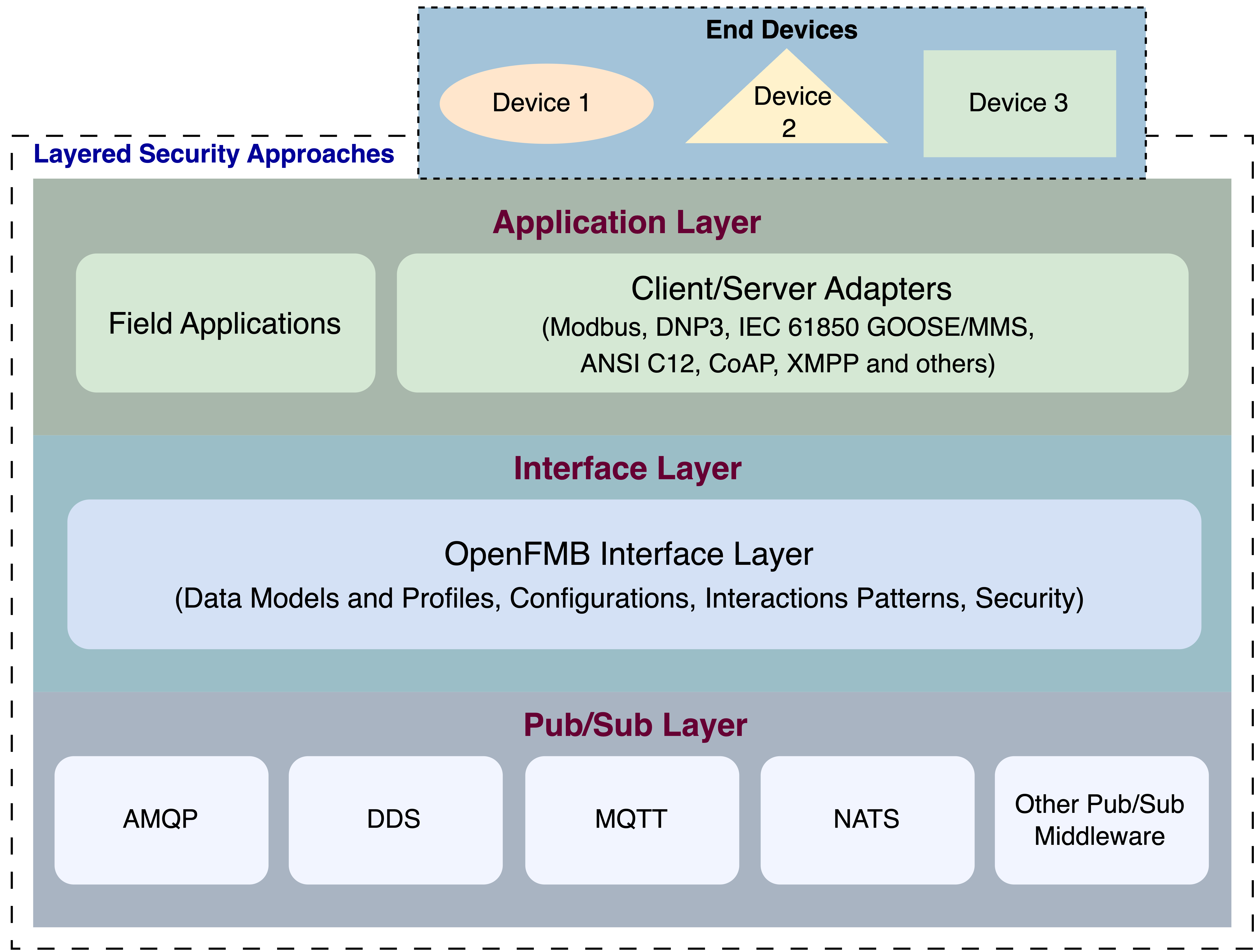
Open-FMB Based Grid
The Open-FMB Based Grid is designed to enhance flexibility, interoperability, and efficiency in energy management systems.
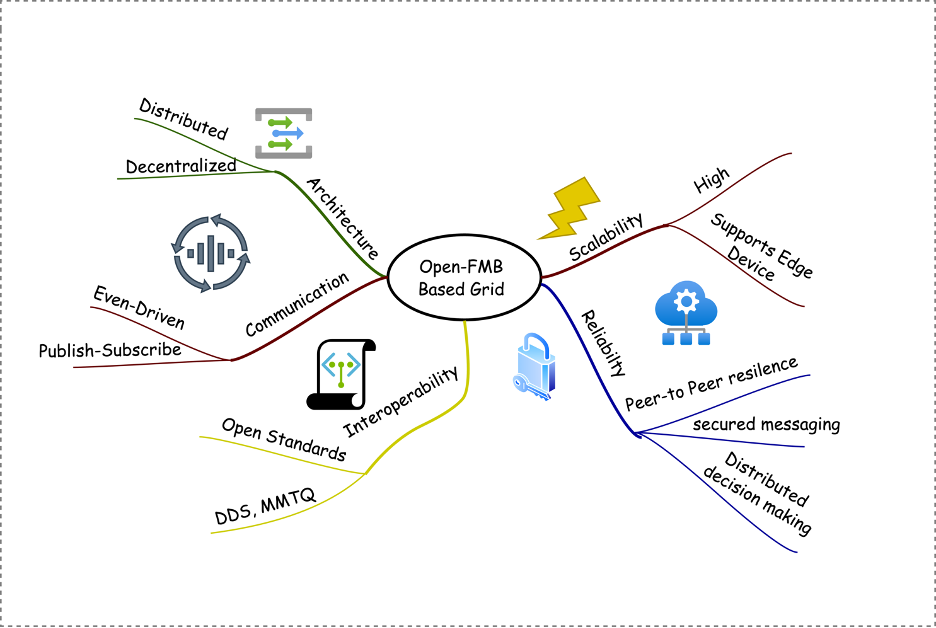
Key Features:
-
Distributed and Decentralized Architecture: The Open-FMB framework is built upon a distributed and decentralized architecture, promoting localized decision-making and minimizing reliance on centralized control systems. This structure allows for enhanced adaptability and rapid response to changing conditions in the energy landscape.
-
Event-Driven Communication: The communication model is event-driven, utilizing a publish-subscribe mechanism that facilitates asynchronous message exchanges. This model allows devices to send and receive updates efficiently, ensuring real-time responsiveness.
-
Interoperability: The framework emphasizes interoperability among diverse devices and systems by leveraging open standards such as DDS (Data Distribution Service) and MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport). This ensures that equipment from various manufacturers can work together seamlessly.
-
Scalability: Open-FMB is designed for high scalability, allowing the system to grow and adapt without compromising performance. This is crucial in accommodating the increasing number of edge devices and data sources as the energy grid evolves.
-
Reliability and Peer-to-Peer Resilience: With a focus on reliability, the Open-FMB architecture provides mechanisms for secure messaging between devices. The peer-to-peer structure enhances resilience, allowing for uninterrupted communication even if individual components fail.
-
Support for Edge Devices: The architecture supports a wide range of edge devices, facilitating the integration of sensors, controllers, and other local elements that can actively participate in energy management and monitoring.
-
Distributed Decision Making: By enabling distributed decision-making, the Open-FMB Grid supports more efficient and localized responses to grid conditions, allowing for quicker adjustments based on real-time data.